What is Automated Evidence Collection and Why You Need It?

Ritika Jain
Oct 04, 2024


Compliance is no longer a nice-to-have but a critical necessity for organizations of all sizes in today's complex regulatory landscape. The need to demonstrate compliance with all the applicable regulations is more important than ever.
While there are other important aspects of a compliance program, evidence collection, which involves gathering and maintaining documentation that demonstrates an organization’s adherence to regulatory standards, tops the list. As a compliance program grows, evidence collection can become increasingly complex, time-consuming, and burdensome.
This blog digs into what evidence collection is, the challenges associated with manual processes, and how automated evidence collection can streamline compliance efforts.
What is Evidence Collection for Compliance?
Evidence collection in the context of regulatory compliance refers to the process of gathering, documenting, and organizing proof that an organization adheres to specific regulatory standards, security frameworks, and industry requirements. This evidence can include everything from policy documents to system logs, all of which are crucial for passing audits and demonstrating compliance.
Proper evidence collection not only proves compliance but also helps in identifying gaps, mitigating risks, and maintaining trust with customers, partners, and regulators.
What Evidence Must Be Collected for Compliance?
The evidence collected can vary widely depending on the specific regulatory requirements but generally includes documentation such as policies, logs, records, and reports. The following is a detailed list of the most common types of evidence required:

1. Policies and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): These are documented guidelines that outline how an organization operates. They are crucial for establishing consistent practices and demonstrating compliance with various regulatory standards.
2. Audit Trails and Logs: Audit trails and system logs help track user activities, system access, and changes made within an organization’s IT environment. They are essential for ensuring accountability and detecting potential security breaches.
3. Testing Reports: These reports demonstrate that systems, processes, and controls have been tested and validated against compliance requirements, ensuring they function as intended.
4. Incident Response Plans: Documented plans for responding to security incidents are critical. They show that an organization is prepared to handle breaches and other security events effectively.
5. Change Management Policies: These documents outline how changes to systems, processes, or controls are managed to ensure they do not negatively impact security or compliance.
6. Risk Assessments: Regular risk assessments help organizations identify, evaluate, and mitigate potential threats. Documentation of these assessments is often required to prove ongoing risk management efforts.
7. Training Records: Compliance often requires that employees undergo specific training to ensure they are aware of regulatory requirements and security protocols. Training records serve as proof that these educational activities have been completed.
8. Third-Party Agreements: Compliance often extends to third-party vendors and partners. Documenting agreements with these entities is essential for ensuring that they also adhere to relevant regulations.
The Challenges of Manual Evidence Collection
Manual evidence collection involves a significant amount of manual effort to gather, organize, and document information. This approach can lead to several challenges:
- Time-Consuming: Collecting and organizing evidence manually can be incredibly time-consuming, especially for larger organizations with extensive compliance requirements.
- Error-Prone: Manual processes are susceptible to human errors, which can result in incomplete or incorrect evidence being collected.
- Resource-Intensive: Manual evidence collection requires substantial resources, including personnel and time, which could be better utilized elsewhere.
Activities Involved
Manual evidence collection involves several activities, including:
- Document Review: Manually reviewing and verifying the accuracy of documents.
- Data Entry: Manually inputting compliance-related data into spreadsheets, databases, or other tracking systems for record-keeping.
- Interviews and Surveys: Conducting interviews and surveys with employees, stakeholders, and third-party vendors to gather necessary information about compliance practices and controls.
- Manual Testing and Audits: Performing compliance tests and audits to assess compliance posture.
- Email and Communication Tracking: PManually tracking relevant communications for evidence purposes.
- Manual Record Keeping: Keeping track of records manually, which can lead to inaccuracies.
- Manual Remediation and Follow-Up: Addressing compliance issues and following up on them manually, which is resource-intensive and slow.
What is Automated Evidence Collection?
Automated evidence collection refers to the use of technology and software solutions to automatically gather, organize, and manage compliance-related evidence. The automated evidence collection systems work by integrating with an organization’s existing IT infrastructure, security tools, and applications. They continuously monitor and collect evidence, such as logs, reports, and access records, and organize them in a centralized system for easy access and reporting.
SOC 2 Compliance Checklist Ultimate Guide
Fast-forward your journey to SOC 2 compliance & build the trust with your customers and stakeholders.
Businesses Benefits of Automated Evidence Collection
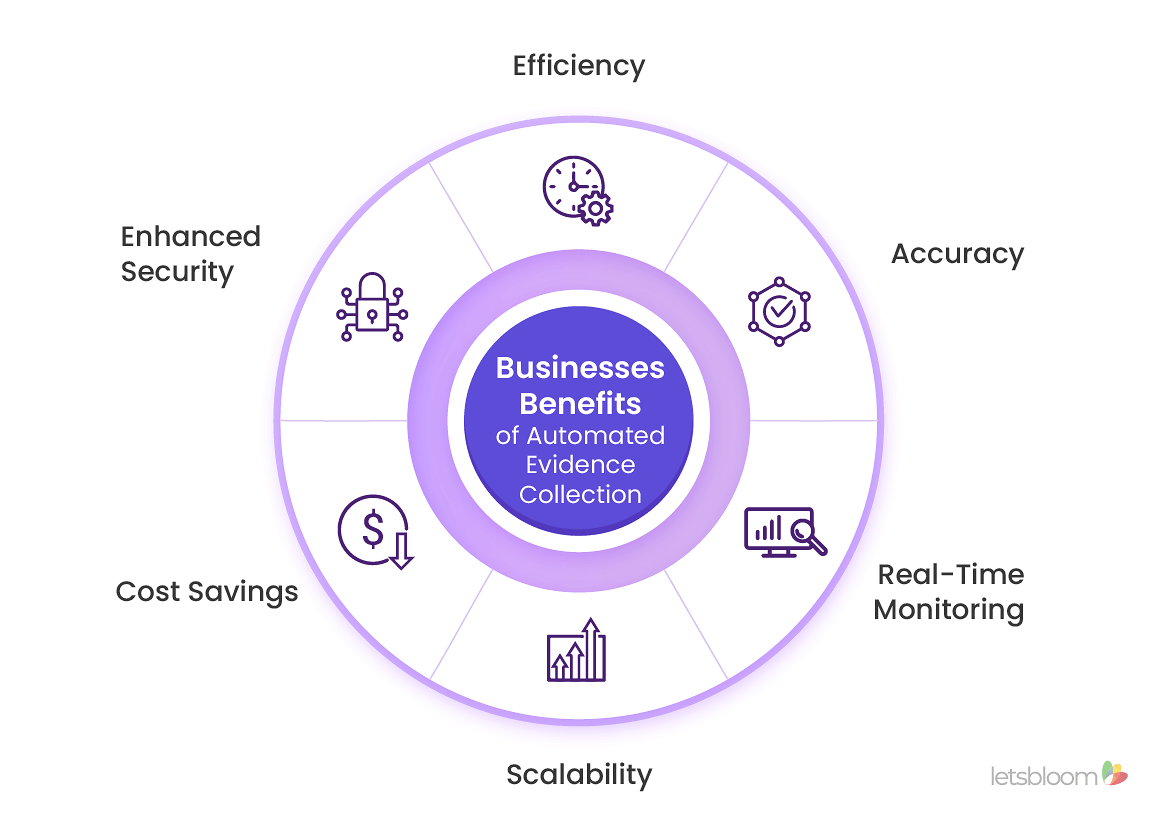
In the context of modern compliance requirements, automated evidence collection is crucial for organizations looking to streamline their compliance processes, reduce errors, and minimize the resources required for evidence collection. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Efficiency: Automation significantly reduces the time and effort required for evidence collection, freeing up resources for other critical tasks.
2. Accuracy: These are documented guidelines that outline how an organization operates. They are crucial for establishing consistent practices and demonstrating compliance with various regulatory standards.
3. Real-Time Monitoring: Automated evidence collection enables real-time monitoring and reporting, providing organizations with up-to-date compliance status and early detection of potential issues.
4. Scalability: As a compliance program grows, automated systems can easily scale to handle the increased volume of evidence collection without requiring additional manual effort.
5. Cost Savings: By reducing manual labor and increasing efficiency, organizations can achieve significant cost savings in their compliance efforts.
6. Enhanced Security: Automation enhances security by ensuring consistent and thorough evidence collection, reducing the likelihood of gaps that could lead to compliance failures.
The future of compliance will undoubtedly involve more automation as organizations seek to keep pace with ever-changing regulations and standards. Embracing automated evidence collection is a critical step toward achieving sustainable, efficient, and smarter compliance management.
Partner with letsbloom today and automate your compliance journey with AI-powered compliance management platform!










